Table of contents
Table of contents
What is a Strategy Map?

Summary
In this guide, you will learn:
What a strategy map is: a visual tool that outlines an organization’s goals, strategies, and initiatives to provide a high-level overview of how to achieve success
The benefits of strategy maps, including enhanced strategic alignment across teams, improved communication, and clear visualization of objectives and their relationships
How strategy maps help identify and prioritize key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and support data-driven decision-making
The role of strategy maps in fostering collaboration by providing a shared vision and helping stakeholders understand how their efforts contribute to overall goals
How strategy maps facilitate tracking progress and enable organizations to adjust strategies as needed to stay on course
Tips for creating your own strategy map tailored to your organization’s specific goals and objectives, emphasizing that there is no one-size-fits-all approach
Introduction to Strategy Maps
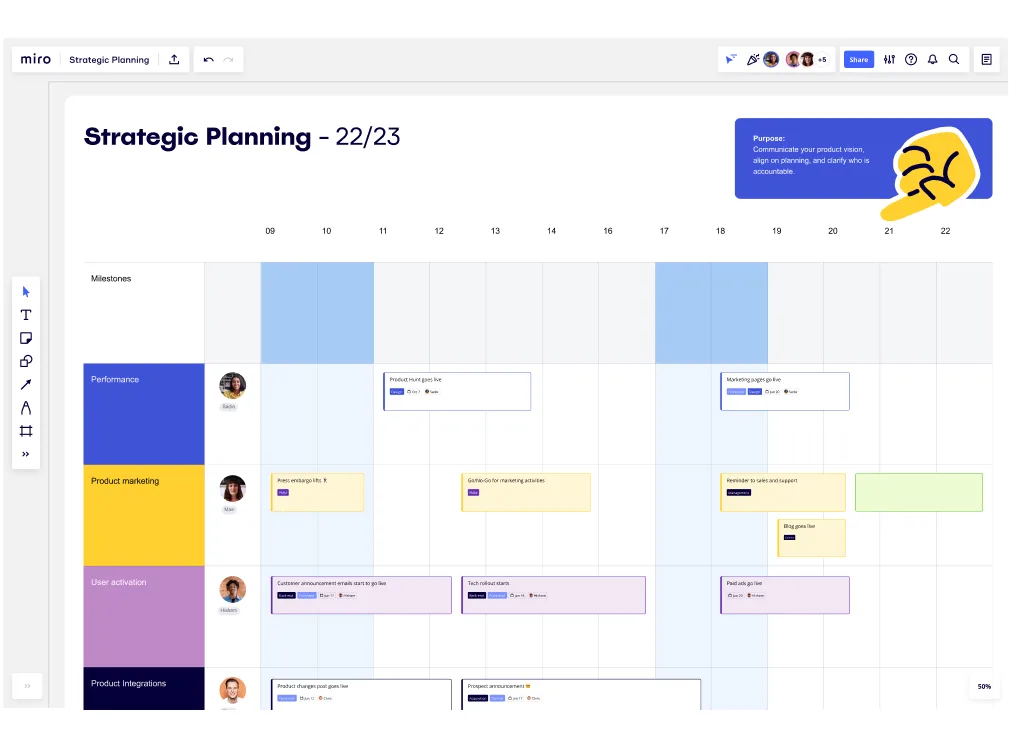
A strategy map serves as a comprehensive and visually compelling framework that outlines an organization's strategic objectives and the interconnected relationships between various components. It represents a powerful tool in strategic planning, as it enables businesses to align their efforts, communicate their vision, and achieve their goals effectively.
Key Components of a Strategy Map
Perspectives in a Strategy Map
A strategy map typically comprises four perspectives, each representing a critical aspect of the organization's performance:
• Financial Perspective: This perspective centers on financial objectives and measures that are vital for the organization's success. Financial goals may include increasing revenue, maximizing profitability, managing costs, or improving return on investment (ROI).
• Customer Perspective: The customer perspective focuses on understanding and meeting the needs of the organization's target audience. Objectives here may include enhancing customer satisfaction, increasing customer retention, and building long-lasting relationships.
• Internal Process Perspective: This perspective deals with the critical internal processes and operations that drive business success. It involves streamlining processes, reducing inefficiencies, and enhancing the overall operational effectiveness.
• Learning and Growth Perspective: The learning and growth perspective emphasizes the organization's commitment to continuous improvement and development. It involves nurturing a culture of innovation, investing in employee training and development, and fostering an adaptive and learning-oriented workforce.
Cascading Objectives and Goals
A fundamental feature of a strategy map is its ability to cascade objectives and goals across various perspectives, creating a cause-and-effect relationship between them. The process of cascading involves aligning higher-level strategic objectives with lower-level operational goals to ensure coherence and consistency throughout the organization.
• Linking Objectives across Perspectives: In strategy mapping, it's essential to establish clear links between objectives from different perspectives. For instance, achieving specific financial goals may be directly tied to the successful implementation of certain internal processes and the delivery of exceptional customer service.
• Creating Cause-and-Effect Relationships: By identifying cause-and-effect relationships, strategy maps illustrate how achieving specific objectives in one area contributes to the success of objectives in other areas. This interconnectedness helps foster a unified approach to strategic planning and execution.
Benefits of Using Strategy Maps
The adoption of strategy maps offers numerous advantages to organizations seeking to improve their strategic planning and performance management:
1. Enhanced Strategic Alignment: Strategy maps facilitate alignment across departments and teams, ensuring that everyone in the organization is working toward common strategic objectives. This alignment is crucial for achieving a shared vision and avoiding conflicting priorities.
2. Improved Communication and Understanding: A well-structured strategy map serves as a visual tool to communicate complex strategies in a clear and concise manner. It helps stakeholders at all levels of the organization understand how their efforts contribute to the overall success of the business.
3. Clear Visualization of Objectives and Strategies: By presenting strategic objectives and relationships visually, strategy maps provide stakeholders with a high-level overview of the organization's priorities and the paths to achieving them. This clarity fosters a better grasp of the strategy and promotes a sense of purpose among team members.
4. Focus on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Strategy maps facilitate the identification and prioritization of key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure progress and success. By selecting relevant and meaningful KPIs, organizations can track their performance and make data-driven decisions.
How to Create a Strategy Map
Creating a strategy map involves a systematic approach that combines theoretical understanding with practical implementation using the right tools.
Step 1: Understand the Key Components
Before diving into the specifics, it's essential to grasp the key components of a strategy map, which include financial, customer, internal, and growth perspectives. These perspectives serve as the foundation for a well-structured and interconnected strategic plan.
Step 2: Set Clear and Aligned Objectives
For each perspective, set clear and aligned objectives that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). These objectives should contribute to the overall vision and mission of the organization. Avoid overcomplicating the map with an excessive number of objectives to maintain clarity and focus.
Step 3: Evaluate Productivity and Growth Perspectives
Examine the financial perspective, aligning your strategies to balance business expansion and cost management. Define a few trackable and measurable objectives that will be the main drivers of financial success. Seek buy-in from collaborators and stakeholders to ensure commitment and alignment.
Step 4: Analyze Customer Perspective
Adopt the customer's perspective to understand their needs and preferences fully. Identify key differentiators that set your product or service apart from competitors. Use this analysis to craft customer-centric objectives that focus on enhancing customer satisfaction, loyalty, and overall experience.
Step 5: Delve into Internal Perspective
Take a deep dive into your organization's internal operations, from customer management to internal processes. Evaluate the efficiency of internal flows and identify areas for improvement. Align internal objectives with customer and financial objectives to ensure seamless integration and effectiveness.
Step 6: Explore Growth Perspective
Consider the necessary resources and strategies to achieve the proposed objectives. Reflect on team development, resource allocation, and process improvement. This perspective addresses the vital elements that will support the successful implementation of your strategic plan.
Step 7: Use a Strategy Map Template
Leverage Miro's strategy map template to simplify the process and maintain consistency. These templates offer predefined perspectives, ensuring that your strategy map covers essential aspects of your business.
Step 8: Regularly Review and Update
A strategy map is not a one-time creation but an evolving document. Regularly review and update the map to adapt to changing circumstances and new opportunities. This ensures that the strategy map remains relevant and aligns with the organization's dynamic environment.
Integrating Strategy Maps into Business
Successfully integrating strategy maps into the organization involves several key strategies:
Engage Leadership and Key Stakeholders: The active involvement of leadership and key stakeholders is vital for crafting a strategy map that reflects the organization's vision and goals. By engaging these individuals throughout the process, organizations ensure buy-in and commitment to the strategic plan.
Cascade the Strategy: To operationalize the strategy, organizations must cascade the strategic objectives and goals down to individual teams and employees. Each team's objectives should directly align with higher-level strategic goals, creating a seamless connection between different levels of the organization.
Regularly Review and Update: Strategy mapping is not a one-time exercise but an ongoing process. Regularly reviewing and updating the strategy map enables organizations to adapt to changing circumstances and emerging opportunities or challenges.
Strategy Maps vs. Other Strategic Planning Tools
Comparing strategy maps to other strategic planning tools:
Strategy Maps: Strategy maps provide a more holistic view of the organization's strategy, focusing on the cause-and-effect relationships between objectives. They offer a comprehensive visual representation of the strategic plan, enhancing communication and understanding across the organization.

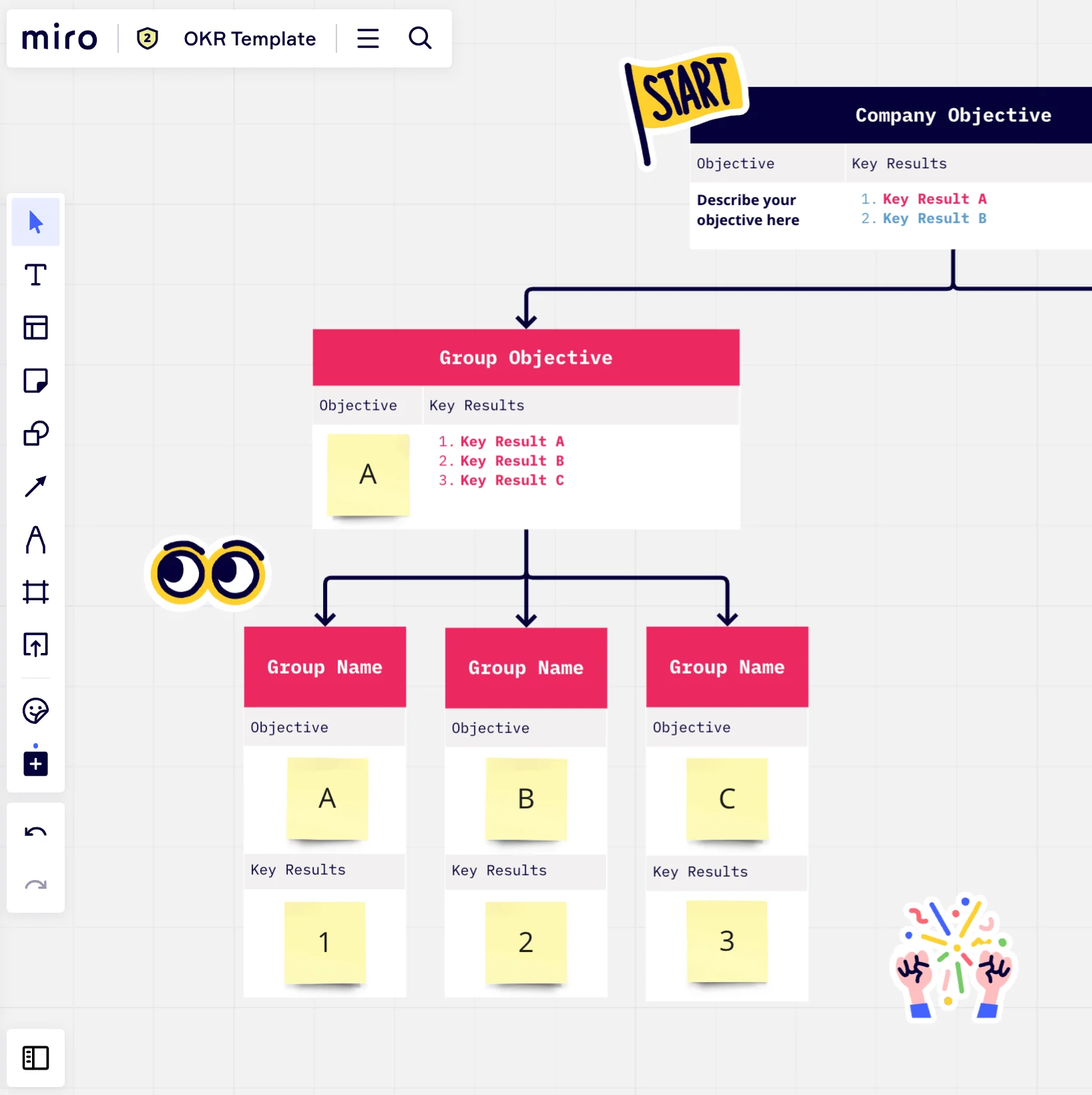
Balanced Scorecards: Balanced scorecards aim to achieve a balance between various performance dimensions, including financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. While both balanced scorecards and strategy maps share some similarities, balanced scorecards may not offer the same depth of cause-and-effect relationships.

OKRs (Objectives and Key Results): OKRs prioritize setting measurable and ambitious objectives with corresponding key results. While effective in focusing teams on specific outcomes, OKRs may lack the comprehensive and interconnected view that strategy maps provide.
Common Mistakes in Using Strategy Maps
Avoiding common pitfalls is essential to ensure the effectiveness of strategy maps:
Neglecting to Align with the Overall Organizational Vision: Strategy maps must align with the broader vision and mission of the organization. Failing to link the strategy map's objectives to the organization's core purpose may lead to disjointed efforts and inefficiencies.
Overcomplicating the Map with Too Many Objectives and Connections: An overly complex strategy map can confuse stakeholders and hinder effective communication. Organizations should focus on a manageable number of critical objectives and clearly depict their interdependencies.
Failing to Update the Map Regularly: A static strategy map can become outdated quickly, rendering it less effective as a planning and management tool. Regularly reviewing and updating the strategy map allows organizations to stay responsive to changing environments and adjust their course as needed.
Final thoughts on strategy maps
In conclusion, a strategy map is a foundational tool for strategic planning and performance management, offering organizations a clear, comprehensive, and interconnected view of their objectives and strategies.
By meticulously defining each perspective and aligning cause-and-effect relationships, organizations can ensure that every aspect of their operations contributes to achieving the overarching strategic goals.
Regularly updating the strategy map and fostering alignment throughout the organization will propel businesses towards sustained success and growth. As organizations continue to embrace strategy maps, they unlock a world of opportunities and strategic clarity, paving the way for excellence and innovation in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Author: Miro Team Last update: August 12, 2025