Table of contents
Table of contents
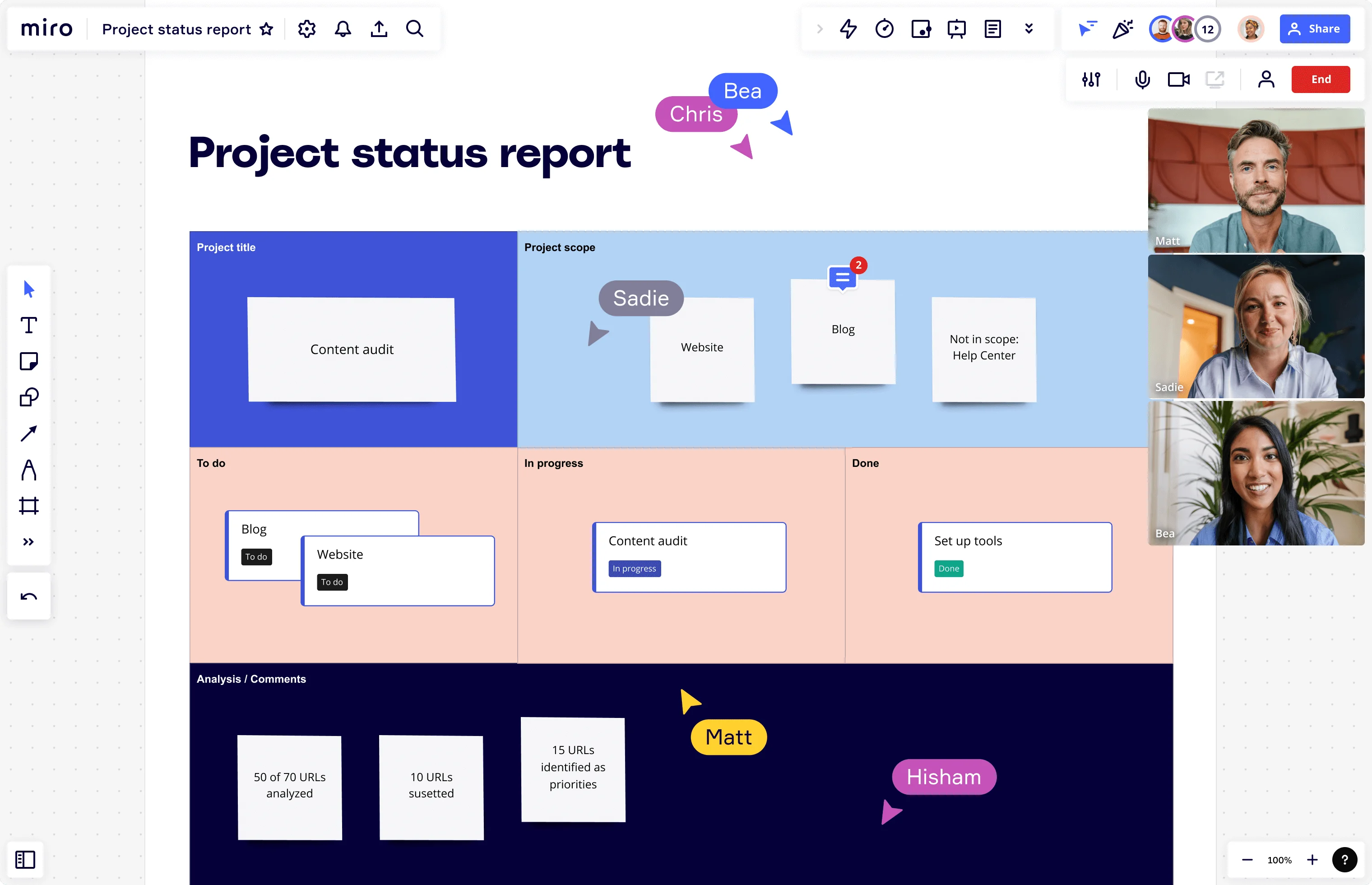
What is a project status report?

Summary
In this guide, you will learn:
What a project status report is: a concise document providing a snapshot of a project's current state and progress
Key components of a project status report: overview, milestones, tasks, resources, risks, issues, decisions, and recommendations
How to visually represent project progress and budget using charts and dashboards
The importance of including schedule, budget, scope, quality, and communication status for comprehensive reporting
Typical formats and frequencies for status reports, from written documents to presentations or dashboards, with daily to monthly intervals
Best practices for structuring reports with executive summaries, clear next steps, and relevant metrics
Try Miro now
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Project status reports: Key components to include
Project status reports serve as essential communication tools in project management. They play a crucial role in providing stakeholders and team members with valuable insights into the progress, performance, risks, and issues related to the project.
There are many good reasons to regularly provide status reports during the course of a project, such as:
Progress and performance
The most pertinent aspect of a project status report is that it provides a clear and concise overview of the project's progress and performance. It aims to convey the current state of the project, highlighting accomplished milestones, completed tasks, and any ongoing activities. The report will also include a comparison of planned progress against actual progress to identify any potential deviations.
Identify risks and issues
Project status reports are also used to identify and evaluate potential risks and issues that could impact the project's success. Additionally, the report should outline the strategies and contingency plans put in place to mitigate these risks and address any issues that have arisen.
Align stakeholders and team members
Status reports are an easy way to keep stakeholders and team members informed and aligned with the project's objectives and direction. In addition to the current status of the project, the report should cover critical data points, key insights, and performance trends, to enable project managers and other stakeholders to assess the project's health and make adjustments as needed to keep it on track.
Key components of a project status report
A well-structured project status report consists of several key components that provide a comprehensive view of the project's status. The main sections are as follows:
Project overview
The project overview section sets the foundation for the entire report. It includes essential information about the project, such as its name, unique ID or reference number, project manager's name, and team members involved. Additionally, it outlines the project's duration and expected timeline for completion.
Progress summary
The progress summary section offers a concise summary of the project's current state. It provides an overview of the overall progress, highlighting major accomplishments, completed milestones, and ongoing tasks. This section aims to give readers a quick understanding of where the project stands.
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
In this section, the report delves into specific performance metrics that measure the project's success. It includes relevant KPIs, such as productivity, efficiency, quality, and adherence to schedule and budget. By tracking and analyzing KPIs, project managers can assess project performance objectively.
Risks and issues
This section identifies potential risks and issues that could impact the project's progress. It provides a detailed analysis of each risk, including its potential impact on the project and the likelihood of occurrence. Additionally, it outlines the mitigation and contingency plans in place to handle these risks.
Budget and resource allocation
This section focuses on the financial aspect of the project. It provides an overview of the project budget, including planned versus actual expenditure. It also examines resource allocation and utilization to ensure that resources are being used effectively to achieve project goals.
Changes and scope creep
The changes and scope creep section addresses any modifications to the project's scope and requirements. It outlines the reasons behind scope changes, tracks the status of change requests, and evaluates their impact on the project's timeline and budget.
Stakeholder communication
This section highlights the importance of effective stakeholder communication and engagement. It includes a stakeholder engagement plan, details on how stakeholders are being kept informed, and any feedback or concerns expressed by stakeholders. Additionally, it measures stakeholder satisfaction with the project's progress.
Types of project status reports
Project status reports can vary in frequency and level of detail based on the project's size, complexity, and stakeholders' preferences. Different types of project status reports include:
Weekly status reports
Weekly reports provide regular updates on the project's progress, issues, and upcoming tasks. They are concise and focus on recent developments. These reports help keep team members and stakeholders informed on a frequent basis and facilitate quick decision-making.
Monthly or bi-monthly reports
Monthly or bi-monthly reports offer a more comprehensive view of the project's progress over a more extended period. They include in-depth analyses of key performance indicators, risks, and budget utilization. These reports are often used for higher-level stakeholders and management.
Quarterly reports
Quarterly reports are broader and more strategic in nature. They review the project's performance, achievements, and challenges over the quarter. These reports often include a more in-depth analysis of project outcomes, trends, and long-term planning.
Ad-hoc reports
Ad-hoc reports are requested on an as-needed basis and are not part of the regular reporting schedule. These reports address specific concerns or incidents that require immediate attention. They provide flexibility in addressing urgent issues outside the standard reporting timeline.
The choice of which type of report to use depends on the project's specific requirements and the needs of the stakeholders involved. Regular communication through status reports is critical to ensure transparency, accountability, and successful project delivery.
Author: Miro Team
Last update: October 16, 2025