Table of contents
Table of contents
Your Guide to Product Management

Summary
In this guide, you will learn:
What product management is and the role it plays in turning ideas into successful products
The responsibilities of a Product Manager and how they guide a product’s lifecycle
The key steps in the product management workflow, from research to launch and iteration
Best practices for Product Managers, including Agile methodologies, data-driven decision making, and essential tools
How collaborative platforms like Miro can support roadmapping, brainstorming, and cross-functional alignment
Try Miro now
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
When trying to build successful products, challenges always arise. It’s just part of the process. From wasted resources and unclear priorities to team misalignment and a lack of a clear strategy, product management isn’t easy.
But product management doesn’t always need to lead to failure. Excelling as a Product Manager (PM) goes beyond just knowing your product. It’s about mastering leadership, communication, and strategy.
Whether you're steering a product development team or working closely with agile teams, understanding the core principles of product management can set you apart.
What is product management?
At its core, product management is about overseeing a product’s journey, from initial idea to market launch and beyond. It’s a strategic function that involves deeply understanding customer needs, defining a clear product vision, and collaborating with cross-functional teams to bring that vision to life.
Why is product management important?
Product management is important for ensuring the right products are built efficiently and strategically. When done successfully, product management aligns teams, reduces friction, and helps focus on outcomes that matter.
Without effective product management, companies risk building products or features that don’t solve real problems, wasting resources and falling short of the competition.
Strong product management helps align cross-functional teams around a shared vision and strategy. This reduces friction, accelerates decision-making, and creates clarity in day-to-day execution. A good Product Manager keeps everyone moving in the same direction, from engineering and design to marketing and sales.
It also drives competitiveness. In markets where speed and innovation matter, product management ensures businesses stay ahead by delivering features and experiences that truly resonate with users. In short, it’s the difference between guessing what customers want and consistently delivering value that makes a measurable impact.
What is a Product Manager?
A Product Manager is a key lynchpin in product management. They act as the bridge between customer needs, business goals, and technical capabilities. Product Managers work closely with cross-functional teams to ensure products can successfully move from idea to finished item.
What does a Product Manager do?
The Product Manager (PM) is responsible for guiding the development and success of a product. They are the strategic lead and decision-maker for a product throughout its entire lifecycle, ensuring the right product is built, in the right way, for the right users. Big boots to fill!
The key responsibilities of a product manager include:
Defining the product vision and strategy, setting a clear direction for the product and aligning stakeholders
Prioritizing what to build, including what features, fixes, and improvements are important
Collaborating across teams, from engineering and design to marketing, sales, and customer support
Representing the user to understand their needs via research and idea testing
Measuring and iterating, using data to define success and continuously improve the product
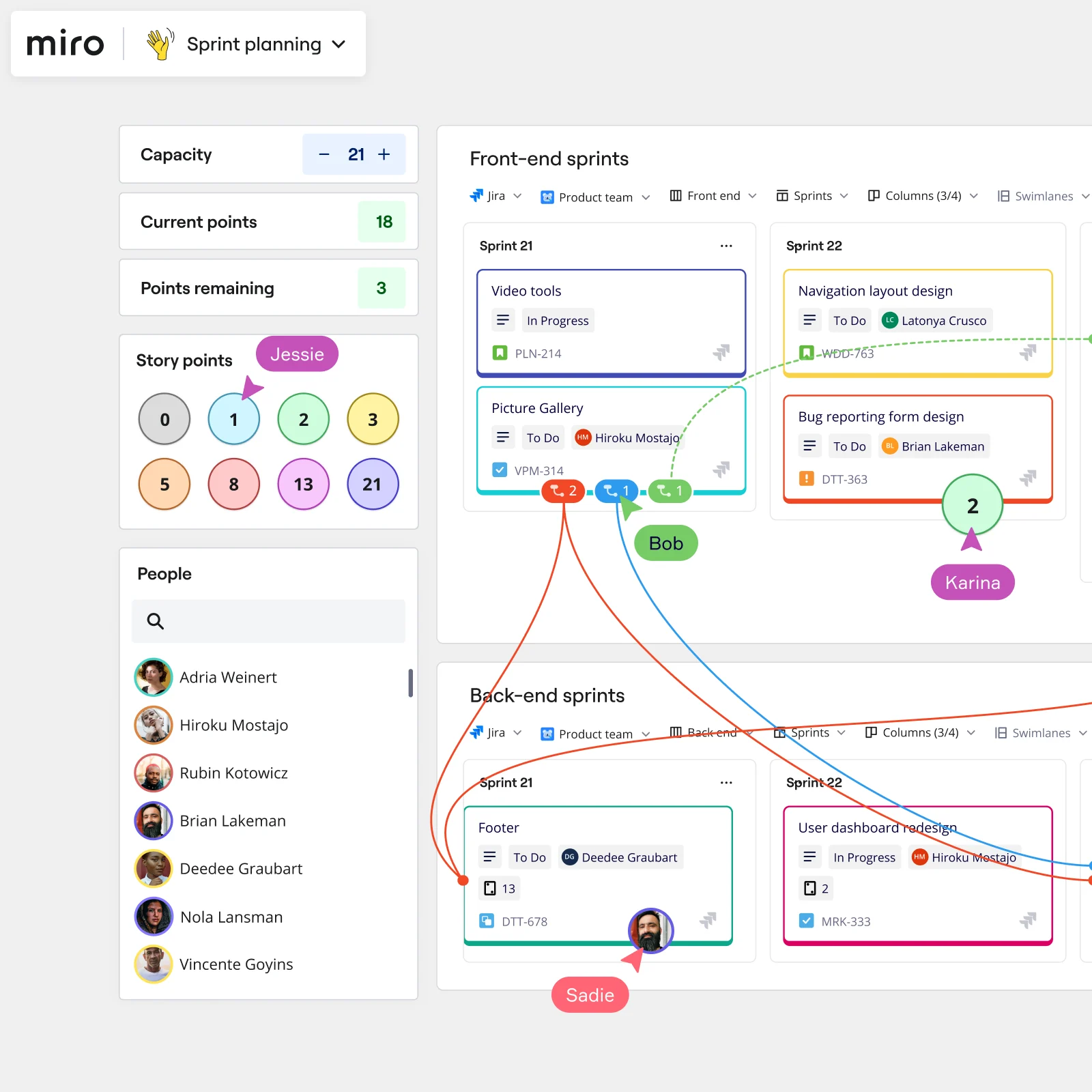
How do Product Managers work with Agile or Scrum teams?
In Agile environments, Product Managers often take on the role of Product Owner. They’ll also work closely with the Scrum Master in Scrum. They maintain the backlog, write user stories, work on sprint planning, and ensure that the product being built meets user needs and the product strategy.
This involves maintaining and prioritizing the product backlog, writing clear user stories, and working with the team during sprint planning to ensure priorities are understood. PMs collaborate closely with the Scrum Master to remove blockers and keep the team focused on outcomes that support the product vision.
Beyond the backlog, Product Managers must continuously gather customer feedback, analyze data, and adjust priorities to keep the team aligned with real-world needs. In Kanban settings, they work to visualize workflows and manage work-in-progress, making sure that bottlenecks are identified and addressed quickly.
Ultimately, their role isn’t just about process, it’s about making sure that the Agile team is building the right things, not just building things fast.
The product lifecycle
The product lifecycle forms the backbone of product management. It consists of five key stages, each essential for the success of a product.
Development
This is where ideas are born, and concepts are validated. PMs must ensure the product aligns with market needs and is feasible to develop. Engaging early with potential customers provides insights that shape the product’s trajectory.
Product Managers should identify real user problems through customer interviews, market research, and competitive analysis. Another key part of this stage is developing a clear product vision and testing assumptions through prototypes or MVPs (minimum viable products).
Introduction
After development, the focus shifts to launching the product. This includes developing go-to-market plans, training internal teams, and running beta tests or early access programs.
PMs must work closely with marketing and customer service teams to position the product effectively. Creating awareness through targeted marketing and gathering early user feedback are essential for refining and improving the offering.
Growth
As the product gains traction, scaling operations and optimizing revenue become priorities. For a PM, this could involve expanding features based on user feedback, entering new market segments, or improving onboarding flows to reduce friction.
It’s also important for PMs to identify opportunities for monetization, upselling, or increasing lifetime value (LTV) during this stage. Retention, engagement, and NPS should all be tracked throughout the process to ensure data-driven decisions can be made.
Maturity
During this stage, PMs aim to maximize profitability and extend the product’s relevance. The focus here is on maintaining interest among the customer base, improving profit margins, and standing out from competitors.
Feature enhancements or localization, as well as tool integrations could help to invigorate growth during the maturity phase.
Decline
From market shifts to newer solutions or internal priority shifts, all products face diminishing demand. When a product approaches the end of its lifecycle, PMs may need to decide whether to revitalize, retire, or replace it.
If a decision to retire the product is made, PMs must plan existing customer support, communications, and technical debt carefully.
For more on product lifecycle management, our guide has got you covered.
Key steps in the product management workflow
The product management workflow consists of several critical phases, each requiring careful planning and execution:
Market Research: PMs gather insights into customer preferences, market trends, and competitors to identify opportunities and risks.
Product Strategy: A strong strategy defines the product’s vision, objectives, and success metrics. It serves as a roadmap, keeping teams aligned and focused on delivering customer value.
Design & Development: Working with design and engineering teams, PMs translate customer needs into actionable specifications, ensuring a seamless development process.
Launch & Iteration: A successful product launch demands coordination across marketing, sales, and support teams. Post-launch, PMs must monitor performance and continuously iterate based on feedback.
How do Product Managers prioritize features?
When evaluating and ranking features based on user value, Product Managers can use a number of frameworks to prioritize features. These may include:
RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort)
MoSCoW (Must, Should, Could, Won’t)
Kano Model
However, prioritization is not a one-off exercise. It requires continuous refinement based on new data, changing market conditions, and customer feedback. Strong PMs also know that prioritization isn’t just about frameworks, it’s about making tough trade-offs and clearly communicating the reasoning to stakeholders. This transparency helps build trust and keeps teams aligned.
Product Manager Best Practices
To become an excellent Product Manager, focus on continuous learning, building strong relationships, and leveraging feedback.
Stay informed by keeping up with industry trends, exploring new methodologies, and networking with peers.
Foster trust by understanding your team and stakeholders’ perspectives and involving them in decision-making.
Create feedback loops with customers and team members to refine your product strategy.
Adopting these best practices can elevate your product management game.
Here are some essential extra tips for product managers:
Embrace Agile Product Management
Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, empower teams to adapt quickly and stay customer-focused.
Agile emphasizes iterative development, collaboration, and early delivery.
Scrum involves structured sprints, while Kanban visualizes workflows to improve efficiency.
By leveraging Agile principles, PMs can respond to changing demands and continuously deliver value.
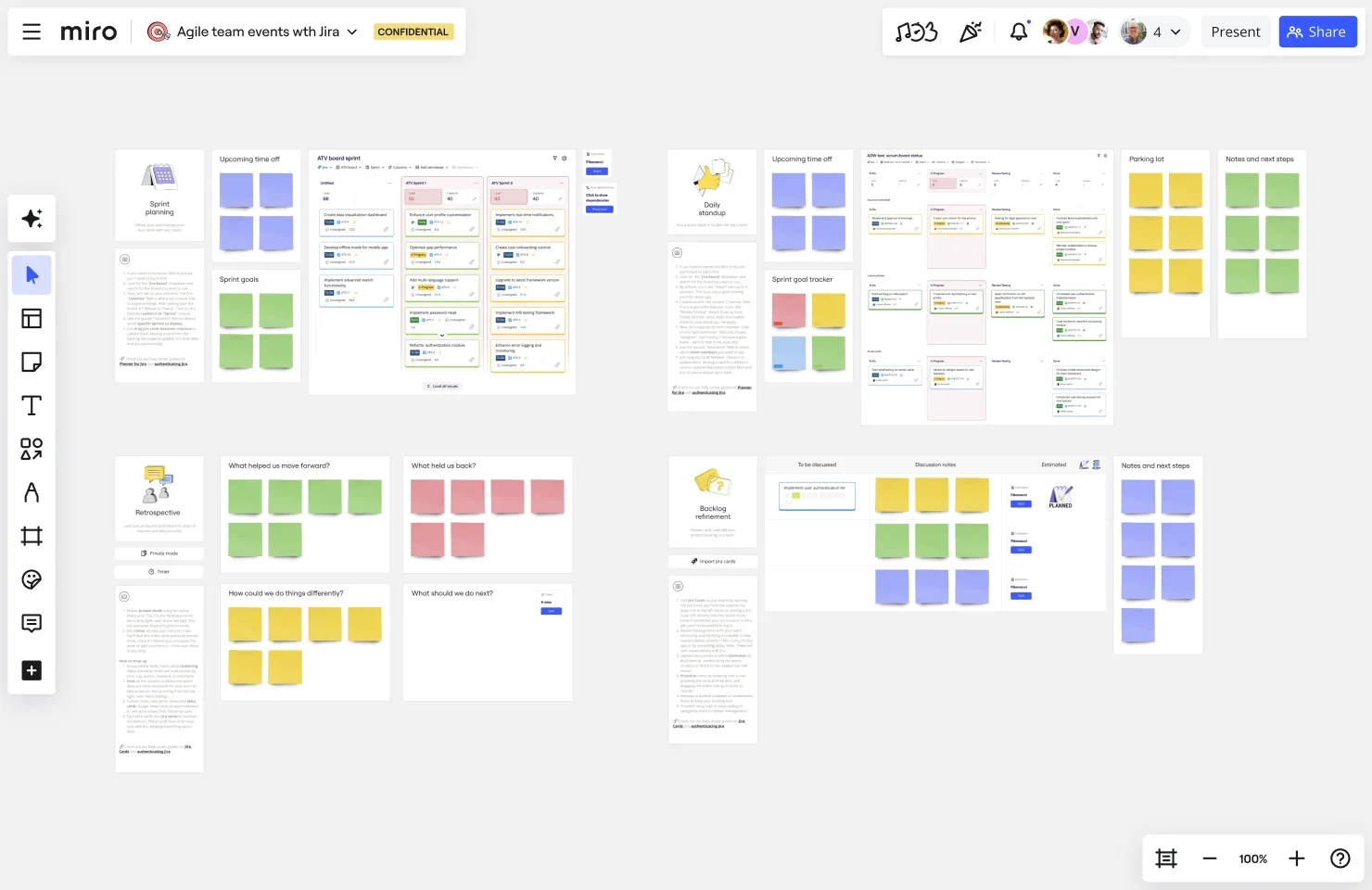
Use the right tools
The best product manager tools streamline collaboration and simplify complex processes. For example, Miro supports brainstorming, roadmapping, and design sprints with features designed for both real-time and asynchronous collaboration.
Here are some common product management tools used by PMs:
Miro: Facilitates brainstorming, roadmapping, and design sprints with visual collaboration features.
Jira: Manages agile workflows, sprints, and issue tracking for development teams.
Trello: Simplifies task and project management with a Kanban-style board system.
Asana: Organizes tasks, tracks progress, and enhances team productivity.
Notion: Combines note-taking, task management, and documentation in a unified workspace.
Figma: Supports design collaboration, prototyping, and UI/UX design iteration.
Google Analytics: Offers insights into user behavior and website performance for data-driven decisions.
Amplitude: Tracks user behavior and engagement metrics to optimize product experiences.
Slack: Enhances team communication with real-time messaging and integration capabilities.
Confluence: Centralizes team documentation and knowledge sharing.
Zoom: Supports remote meetings and collaboration through video conferencing.
Mixpanel: Analyzes user interactions and tracks metrics for improved engagement strategies.
You can see how a project manager uses Miro to plan a product strategy in this video.
Data-driven decisions
Data is an invaluable tool for PMs keen to follow successful product management principles. Using data drives informed decisions and validates assumptions.
Collect & Analyze: PMs must harness data from user analytics, customer feedback, and sales reports to uncover trends and behaviors.
Drive Decisions: By understanding what users value most, PMs can prioritize features and focus on impactful developments.
Iterate & Improve: Regularly reviewing data allows PMs to fine-tune the product, ensuring it evolves with user needs.

What to consider when choosing product management tools?
When choosing product management tools, you need to consider what features matter the most to your business. Think about:
Ease of use: Tools should be intuitive enough that teams adopt them quickly without heavy training.
Scalability: As your product grows, the tool should support more complex workflows and larger teams.
Collaboration capabilities: Look for platforms that make it easy to share updates, align stakeholders, and centralize communication.
Customization options: Every product team works differently. A tool that can adapt to your processes is more valuable than one that forces rigid workflows.
Integrations: Strong integrations with your existing tech stack (e.g., Jira, Slack, analytics platforms) save time and reduce context switching.
Security: Ensure tools meet your company’s compliance requirements and protect sensitive data.
Support: Reliable uptime and responsive customer support are critical when your team depends on the tool daily.
Pricing: Cost should align with the value delivered, especially if you’re scaling across a large organization.
Boost your product management routine with Miro
Are you ready to take your product management skills to the next level? Miro offers a collaborative platform tailored for product managers looking to enhance their workflows, streamline communication, and foster innovation within their teams.
With Miro, you can create interactive roadmaps, conduct brainstorming sessions, and facilitate design sprints effortlessly.
Start maximizing your productivity and empowering your teams to achieve outstanding product outcomes today! Sign up for free and join the growing community of product managers transforming their routines with Miro.
Don't just manage products - lead them to success with Miro!
Product management FAQs
How does Miro support product lifecycle management?
Miro can support the entire product lifecycle, from idea discovery and roadmap planning to launch coordination and post-launch optimizations.
When using Miro’s product management software, you can visually track your product’s evolution, connect documentation and feedback, and asynchronously update your team from one place.
Can Miro be used as a complete product management tool?
Miro is a great tool for visual product planning, roadmapping, sprint planning, retrospectives, and user journey mapping. As a complete product management tool, it offers a centralized space for core product management activities, but may be complemented by task tracking and analytics tools.
Is Miro easy for Product Managers to use?
Miro is designed to be intuitive and flexible, making it suitable for any ability. Our drag-and-drop functionality, pre-built templates, and keyboard shortcuts ensure even non-technical Product Managers can use it effectively.
How can I collaborate in Miro for product management?
Product Managers can co-create roadmaps, prioritize features, and align with cross-functional teams in Miro with real-time and async collaboration features. You can also tag team members, add comments, use voting tools, and even facilitate workshops with our built-in templates.
Author: Miro Team
Last update: October 14, 2025